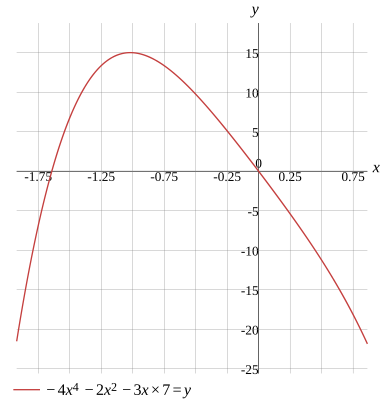
Question
Function
Find the x-intercept/zero
Find the y-intercept
x1≈−1.642221,x2=0
Evaluate
−4x4−2x2−3x×7=y
To find the x-intercept,set y=0
−4x4−2x2−3x×7=0
Multiply the terms
−4x4−2x2−21x=0
Factor the expression
−x(4x3+2x+21)=0
Divide both sides
x(4x3+2x+21)=0
Separate the equation into 2 possible cases
x=04x3+2x+21=0
Solve the equation
x=0x≈−1.642221
Solution
x1≈−1.642221,x2=0
Show Solution

Solve the equation
y=−4x4−2x2−21x
Evaluate
−4x4−2x2−3x×7=y
Multiply the terms
−4x4−2x2−21x=y
Solution
y=−4x4−2x2−21x
Show Solution

Testing for symmetry
Testing for symmetry about the origin
Testing for symmetry about the x-axis
Testing for symmetry about the y-axis
Not symmetry with respect to the origin
Evaluate
−4x4−2x2−3x7=y
Simplify the expression
−4x4−2x2−21x=y
To test if the graph of −4x4−2x2−21x=y is symmetry with respect to the origin,substitute -x for x and -y for y
−4(−x)4−2(−x)2−21(−x)=−y
Evaluate
More Steps


Evaluate
−4(−x)4−2(−x)2−21(−x)
Multiply the terms
−4x4−2(−x)2−21(−x)
Multiply the terms
−4x4−2x2−21(−x)
Multiply the numbers
−4x4−2x2+21x
−4x4−2x2+21x=−y
Solution
Not symmetry with respect to the origin
Show Solution

Find the first derivative
Find the derivative with respect to x
Find the derivative with respect to y
dxdy=−16x3−4x−21
Calculate
−4x4−2x2−3x7=y
Simplify the expression
−4x4−2x2−21x=y
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(−4x4−2x2−21x)=dxd(y)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4x4−2x2−21x)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(−4x4)+dxd(−2x2)+dxd(−21x)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4x4)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−4×dxd(x4)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−4×4x3
Multiply the terms
−16x3
−16x3+dxd(−2x2)+dxd(−21x)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−2x2)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−2×dxd(x2)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−2×2x
Multiply the terms
−4x
−16x3−4x+dxd(−21x)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−21x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−21×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−21×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−21
−16x3−4x−21
−16x3−4x−21=dxd(y)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(y)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(y)×dxdy
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
dxdy
−16x3−4x−21=dxdy
Solution
dxdy=−16x3−4x−21
Show Solution

Find the second derivative
Find the second derivative with respect to x
Find the second derivative with respect to y
dx2d2y=−48x2−4
Calculate
−4x4−2x2−3x7=y
Simplify the expression
−4x4−2x2−21x=y
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(−4x4−2x2−21x)=dxd(y)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4x4−2x2−21x)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(−4x4)+dxd(−2x2)+dxd(−21x)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4x4)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−4×dxd(x4)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−4×4x3
Multiply the terms
−16x3
−16x3+dxd(−2x2)+dxd(−21x)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−2x2)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−2×dxd(x2)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−2×2x
Multiply the terms
−4x
−16x3−4x+dxd(−21x)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−21x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−21×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−21×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−21
−16x3−4x−21
−16x3−4x−21=dxd(y)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(y)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(y)×dxdy
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
dxdy
−16x3−4x−21=dxdy
Swap the sides of the equation
dxdy=−16x3−4x−21
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(dxdy)=dxd(−16x3−4x−21)
Calculate the derivative
dx2d2y=dxd(−16x3−4x−21)
Use differentiation rules
dx2d2y=dxd(−16x3)+dxd(−4x)+dxd(−21)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−16x3)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−16×dxd(x3)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−16×3x2
Multiply the terms
−48x2
dx2d2y=−48x2+dxd(−4x)+dxd(−21)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−4×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−4×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−4
dx2d2y=−48x2−4+dxd(−21)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
dx2d2y=−48x2−4+0
Solution
dx2d2y=−48x2−4
Show Solution

Graph