Question
Solve the equation
x=−4
Evaluate
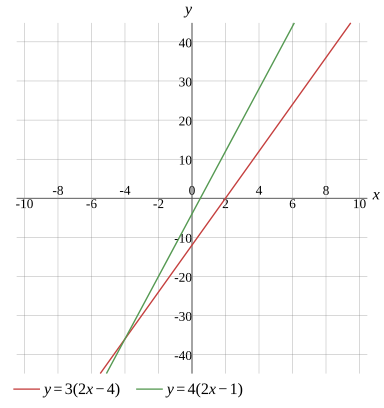
3(2x−4)=4(2x−1)
Calculate
More Steps


Evaluate
3(2x−4)
Apply the distributive property
3×2x−3×4
Multiply the numbers
6x−3×4
Multiply the numbers
6x−12
6x−12=4(2x−1)
Calculate
More Steps


Evaluate
4(2x−1)
Apply the distributive property
4×2x−4×1
Multiply the numbers
8x−4×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
8x−4
6x−12=8x−4
Move the expression to the left side
6x−12−(8x−4)=0
Calculate
More Steps


Add the terms
6x−12−(8x−4)
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
6x−12−8x+4
Subtract the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
6x−8x
Collect like terms by calculating the sum or difference of their coefficients
(6−8)x
Subtract the numbers
−2x
−2x−12+4
Add the numbers
−2x−8
−2x−8=0
Move the constant to the right-hand side and change its sign
−2x=0+8
Removing 0 doesn't change the value,so remove it from the expression
−2x=8
Change the signs on both sides of the equation
2x=−8
Divide both sides
22x=2−8
Divide the numbers
x=2−8
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
2−8
Reduce the numbers
1−4
Calculate
−4
x=−4
Show Solution

Rewrite the equation
x=−4
Evaluate
3(2x−4)=4(2x−1)
Multiply
More Steps


Evaluate
3(2x−4)
Apply the distributive property
3×2x−3×4
Multiply the numbers
6x−3×4
Multiply the numbers
6x−12
6x−12=4(2x−1)
Multiply
More Steps


Evaluate
4(2x−1)
Apply the distributive property
4×2x−4×1
Multiply the numbers
8x−4×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
8x−4
6x−12=8x−4
Move the variable to the left side
−2x−12=−4
Move the constant to the right side
−2x=8
Multiply both sides
2x=−8
Solution
x=−4
Show Solution

Graph