Question
Identify the conic
Find the standard equation of the circle
Find the radius of the circle
Find the center of the circle
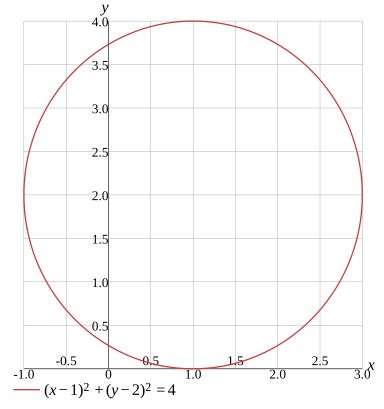
(x−1)2+(y−2)2=4
Evaluate
x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0
Move the constant to the right-hand side and change its sign
x2+y2−2x−4y=0−1
Removing 0 doesn't change the value,so remove it from the expression
x2+y2−2x−4y=−1
Use the commutative property to reorder the terms
x2−2x+y2−4y=−1
To complete the square, the same value needs to be added to both sides
x2−2x+1+y2−4y=−1+1
Use a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2 to factor the expression
(x−1)2+y2−4y=−1+1
Add the numbers
(x−1)2+y2−4y=0
To complete the square, the same value needs to be added to both sides
(x−1)2+y2−4y+4=4
Solution
(x−1)2+(y−2)2=4
Show Solution

Solve the equation
Solve for x
Solve for y
x=1+−y2+4yx=1−−y2+4y
Evaluate
x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0
Rewrite the expression
x2+y2−4y+1−2x=0
Rewrite in standard form
x2−2x+y2−4y+1=0
Substitute a=1,b=−2 and c=y2−4y+1 into the quadratic formula x=2a−b±b2−4ac
x=22±(−2)2−4(y2−4y+1)
Simplify the expression
More Steps


Evaluate
(−2)2−4(y2−4y+1)
Multiply the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
4(y2−4y+1)
Apply the distributive property
4y2−4×4y+4
Multiply the terms
4y2−16y+4
(−2)2−(4y2−16y+4)
Rewrite the expression
22−(4y2−16y+4)
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
22−4y2+16y−4
Evaluate the power
4−4y2+16y−4
Since two opposites add up to 0,remove them form the expression
−4y2+16y
x=22±−4y2+16y
Simplify the radical expression
More Steps


Evaluate
−4y2+16y
Factor the expression
4(−y2+4y)
The root of a product is equal to the product of the roots of each factor
4×−y2+4y
Evaluate the root
More Steps


Evaluate
4
Write the number in exponential form with the base of 2
22
Reduce the index of the radical and exponent with 2
2
2−y2+4y
x=22±2−y2+4y
Separate the equation into 2 possible cases
x=22+2−y2+4yx=22−2−y2+4y
Simplify the expression
More Steps


Evaluate
x=22+2−y2+4y
Divide the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
22+2−y2+4y
Rewrite the expression
22(1+−y2+4y)
Reduce the fraction
1+−y2+4y
x=1+−y2+4y
x=1+−y2+4yx=22−2−y2+4y
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
x=22−2−y2+4y
Divide the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
22−2−y2+4y
Rewrite the expression
22(1−−y2+4y)
Reduce the fraction
1−−y2+4y
x=1−−y2+4y
x=1+−y2+4yx=1−−y2+4y
Show Solution

Testing for symmetry
Testing for symmetry about the origin
Testing for symmetry about the x-axis
Testing for symmetry about the y-axis
Not symmetry with respect to the origin
Evaluate
x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0
To test if the graph of x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0 is symmetry with respect to the origin,substitute -x for x and -y for y
(−x)2+(−y)2−2(−x)−4(−y)+1=0
Evaluate
More Steps


Evaluate
(−x)2+(−y)2−2(−x)−4(−y)+1
Multiply the numbers
(−x)2+(−y)2+2x−4(−y)+1
Multiply the numbers
(−x)2+(−y)2+2x+4y+1
Rewrite the expression
x2+(−y)2+2x+4y+1
Rewrite the expression
x2+y2+2x+4y+1
x2+y2+2x+4y+1=0
Solution
Not symmetry with respect to the origin
Show Solution

Find the first derivative
Find the derivative with respect to x
Find the derivative with respect to y
dxdy=y−2−x+1
Calculate
x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(x2+y2−2x−4y+1)=dxd(0)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(x2+y2−2x−4y+1)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(x2)+dxd(y2)+dxd(−2x)+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
2x+dxd(y2)+dxd(−2x)+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(y2)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(y2)×dxdy
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
2ydxdy
2x+2ydxdy+dxd(−2x)+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−2x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−2×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−2×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−2
2x+2ydxdy−2+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4y)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(−4y)×dxdy
Evaluate the derivative
−4dxdy
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy+dxd(1)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy+0
Evaluate
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy=dxd(0)
Calculate the derivative
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy=0
Collect like terms by calculating the sum or difference of their coefficients
2x−2+(2y−4)dxdy=0
Move the constant to the right side
(2y−4)dxdy=0−(2x−2)
Subtract the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
0−(2x−2)
Removing 0 doesn't change the value,so remove it from the expression
−(2x−2)
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
−2x+2
(2y−4)dxdy=−2x+2
Divide both sides
2y−4(2y−4)dxdy=2y−4−2x+2
Divide the numbers
dxdy=2y−4−2x+2
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
2y−4−2x+2
Rewrite the expression
2y−42(−x+1)
Rewrite the expression
2(y−2)2(−x+1)
Reduce the fraction
y−2−x+1
dxdy=y−2−x+1
Show Solution

Find the second derivative
Find the second derivative with respect to x
Find the second derivative with respect to y
dx2d2y=y3−6y2+12y−8−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
Calculate
x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(x2+y2−2x−4y+1)=dxd(0)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(x2+y2−2x−4y+1)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(x2)+dxd(y2)+dxd(−2x)+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
2x+dxd(y2)+dxd(−2x)+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(y2)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(y2)×dxdy
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
2ydxdy
2x+2ydxdy+dxd(−2x)+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−2x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−2×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−2×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−2
2x+2ydxdy−2+dxd(−4y)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−4y)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(−4y)×dxdy
Evaluate the derivative
−4dxdy
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy+dxd(1)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy+0
Evaluate
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy=dxd(0)
Calculate the derivative
2x+2ydxdy−2−4dxdy=0
Collect like terms by calculating the sum or difference of their coefficients
2x−2+(2y−4)dxdy=0
Move the constant to the right side
(2y−4)dxdy=0−(2x−2)
Subtract the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
0−(2x−2)
Removing 0 doesn't change the value,so remove it from the expression
−(2x−2)
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
−2x+2
(2y−4)dxdy=−2x+2
Divide both sides
2y−4(2y−4)dxdy=2y−4−2x+2
Divide the numbers
dxdy=2y−4−2x+2
Divide the numbers
More Steps


Evaluate
2y−4−2x+2
Rewrite the expression
2y−42(−x+1)
Rewrite the expression
2(y−2)2(−x+1)
Reduce the fraction
y−2−x+1
dxdy=y−2−x+1
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(dxdy)=dxd(y−2−x+1)
Calculate the derivative
dx2d2y=dxd(y−2−x+1)
Use differentiation rules
dx2d2y=(y−2)2dxd(−x+1)×(y−2)−(−x+1)×dxd(y−2)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−x+1)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(−x)+dxd(1)
Evaluate the derivative
−1+dxd(1)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
−1+0
Evaluate
−1
dx2d2y=(y−2)2−(y−2)−(−x+1)×dxd(y−2)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(y−2)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(y)+dxd(−2)
Evaluate the derivative
dxdy+dxd(−2)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
dxdy+0
Evaluate
dxdy
dx2d2y=(y−2)2−(y−2)−(−x+1)dxdy
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
dx2d2y=(y−2)2−y+2−(−x+1)dxdy
Calculate
More Steps


Evaluate
(−x+1)dxdy
Apply the distributive property
−xdxdy+1×dxdy
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−xdxdy+dxdy
dx2d2y=(y−2)2−y+2−(−xdxdy+dxdy)
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
dx2d2y=(y−2)2−y+2+xdxdy−dxdy
Use equation dxdy=y−2−x+1 to substitute
dx2d2y=(y−2)2−y+2+x×y−2−x+1−y−2−x+1
Solution
More Steps


Calculate
(y−2)2−y+2+x×y−2−x+1−y−2−x+1
Multiply the terms
(y−2)2−y+2+y−2x(−x+1)−y−2−x+1
Calculate the sum or difference
More Steps


Evaluate
−y+2+y−2x(−x+1)−y−2−x+1
Reduce fractions to a common denominator
−y−2y(y−2)+y−22(y−2)+y−2x(−x+1)−y−2−x+1
Write all numerators above the common denominator
y−2−y(y−2)+2(y−2)+x(−x+1)−(−x+1)
Multiply the terms
y−2−(y2−2y)+2(y−2)+x(−x+1)−(−x+1)
Multiply the terms
y−2−(y2−2y)+2y−4+x(−x+1)−(−x+1)
Multiply the terms
y−2−(y2−2y)+2y−4−x2+x−(−x+1)
Calculate the sum or difference
y−2−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
(y−2)2y−2−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
Multiply by the reciprocal
y−2−y2+4y−5−x2+2x×(y−2)21
Multiply the terms
(y−2)(y−2)2−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
Multiply the terms
(y−2)3−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
Expand the expression
More Steps


Evaluate
(y−2)3
Use (a−b)3=a3−3a2b+3ab2−b3 to expand the expression
y3−3y2×2+3y×22−23
Calculate
y3−6y2+12y−8
y3−6y2+12y−8−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
dx2d2y=y3−6y2+12y−8−y2+4y−5−x2+2x
Show Solution

Rewrite the equation
r=cos(θ)+2sin(θ)+3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)r=cos(θ)+2sin(θ)−3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
Evaluate
x2+y2−2x−4y+1=0
To convert the equation to polar coordinates,substitute x for rcos(θ) and y for rsin(θ)
(cos(θ)×r)2+(sin(θ)×r)2−2cos(θ)×r−4sin(θ)×r+1=0
Factor the expression
(cos2(θ)+sin2(θ))r2+(−2cos(θ)−4sin(θ))r+1=0
Simplify the expression
r2+(−2cos(θ)−4sin(θ))r+1=0
Solve using the quadratic formula
r=22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)±(−2cos(θ)−4sin(θ))2−4×1×1
Simplify
r=22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)±12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Separate the equation into 2 possible cases
r=22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)+12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)r=22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)−12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Evaluate
More Steps


Evaluate
22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)+12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Simplify the root
More Steps


Evaluate
12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Factor the expression
4(3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ))
Write the number in exponential form with the base of 2
22(3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ))
Calculate
23sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)+23sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
Factor
22(cos(θ)+2sin(θ)+3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ))
Reduce the fraction
cos(θ)+2sin(θ)+3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
r=cos(θ)+2sin(θ)+3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)r=22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)−12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)−12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Simplify the root
More Steps


Evaluate
12sin2(θ)+8sin(2θ)
Factor the expression
4(3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ))
Write the number in exponential form with the base of 2
22(3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ))
Calculate
23sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
22cos(θ)+4sin(θ)−23sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
Factor
22(cos(θ)+2sin(θ)−3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ))
Reduce the fraction
cos(θ)+2sin(θ)−3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
r=cos(θ)+2sin(θ)+3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)r=cos(θ)+2sin(θ)−3sin2(θ)+2sin(2θ)
Show Solution

Graph