Question
Function
Find the x-intercept/zero
Find the y-intercept
Find the slope
x=−5
Evaluate
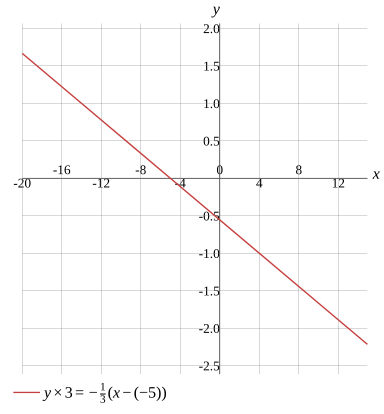
y×3=−31(x−(−5))
To find the x-intercept,set y=0
0×3=−31(x−(−5))
Any expression multiplied by 0 equals 0
0=−31(x−(−5))
Simplify
More Steps


Evaluate
−31(x−(−5))
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
−31(x+5)
Multiply the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
31(x+5)
Apply the distributive property
31x+31×5
Multiply the numbers
31x+35
−(31x+35)
Calculate
−31x−35
0=−31x−35
Swap the sides of the equation
−31x−35=0
Move the constant to the right-hand side and change its sign
−31x=0+35
Add the terms
−31x=35
Change the signs on both sides of the equation
31x=−35
Multiply by the reciprocal
31x×3=−35×3
Multiply
x=−35×3
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
−35×3
Reduce the numbers
−5×1
Simplify
−5
x=−5
Show Solution

Solve the equation
Solve for x
Solve for y
x=−9y−5
Evaluate
y×3=−31(x−(−5))
Use the commutative property to reorder the terms
3y=−31(x−(−5))
Simplify
More Steps


Evaluate
−31(x−(−5))
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
−31(x+5)
Multiply the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
31(x+5)
Apply the distributive property
31x+31×5
Multiply the numbers
31x+35
−(31x+35)
Calculate
−31x−35
3y=−31x−35
Swap the sides of the equation
−31x−35=3y
Move the constant to the right-hand side and change its sign
−31x=3y+35
Change the signs on both sides of the equation
31x=−3y−35
Multiply by the reciprocal
31x×3=(−3y−35)×3
Multiply
x=(−3y−35)×3
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
(−3y−35)×3
Apply the distributive property
−3y×3−35×3
Multiply the terms
−9y−35×3
Multiply the numbers
More Steps


Evaluate
−35×3
Reduce the numbers
−5×1
Simplify
−5
−9y−5
x=−9y−5
Show Solution

Testing for symmetry
Testing for symmetry about the origin
Testing for symmetry about the x-axis
Testing for symmetry about the y-axis
Not symmetry with respect to the origin
Evaluate
y3=−31(x−(−5))
Simplify the expression
3y=−31x−35
To test if the graph of 3y=−31x−35 is symmetry with respect to the origin,substitute -x for x and -y for y
3(−y)=−31(−x)−35
Evaluate
−3y=−31(−x)−35
Multiplying or dividing an even number of negative terms equals a positive
−3y=31x−35
Solution
Not symmetry with respect to the origin
Show Solution

Rewrite the equation
Rewrite in polar form
Rewrite in standard form
Rewrite in slope-intercept form
r=−9sin(θ)+cos(θ)5
Evaluate
y×3=−31(x−(−5))
Use the commutative property to reorder the terms
3y=−31(x−(−5))
Evaluate
More Steps


Evaluate
−31(x−(−5))
If a negative sign or a subtraction symbol appears outside parentheses, remove the parentheses and change the sign of every term within the parentheses
−31(x+5)
Multiply the terms
More Steps


Evaluate
31(x+5)
Apply the distributive property
31x+31×5
Multiply the numbers
31x+35
−(31x+35)
Calculate
−31x−35
3y=−31x−35
Multiply both sides of the equation by LCD
3y×3=(−31x−35)×3
Simplify the equation
9y=(−31x−35)×3
Simplify the equation
More Steps


Evaluate
(−31x−35)×3
Apply the distributive property
−31x×3−35×3
Simplify
−x−5
9y=−x−5
Move the expression to the left side
9y+x=−5
To convert the equation to polar coordinates,substitute x for rcos(θ) and y for rsin(θ)
9sin(θ)×r+cos(θ)×r=−5
Factor the expression
(9sin(θ)+cos(θ))r=−5
Solution
r=−9sin(θ)+cos(θ)5
Show Solution

Find the first derivative
Find the derivative with respect to x
Find the derivative with respect to y
dxdy=−91
Calculate
y3=−31(x−(−5))
Simplify the expression
3y=−31x−35
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(3y)=dxd(−31x−35)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(3y)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(3y)×dxdy
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dyd(3y)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
3×dyd(y)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
3×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
3
3dxdy
3dxdy=dxd(−31x−35)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−31x−35)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(−31x)+dxd(−35)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−31x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−31×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−31×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−31
−31+dxd(−35)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
−31+0
Evaluate
−31
3dxdy=−31
Multiply by the reciprocal
3dxdy×31=−31×31
Multiply
dxdy=−31×31
Solution
More Steps


Evaluate
−31×31
To multiply the fractions,multiply the numerators and denominators separately
−3×31
Multiply the numbers
−91
dxdy=−91
Show Solution

Find the second derivative
Find the second derivative with respect to x
Find the second derivative with respect to y
dx2d2y=0
Calculate
y3=−31(x−(−5))
Simplify the expression
3y=−31x−35
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(3y)=dxd(−31x−35)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(3y)
Use differentiation rules
dyd(3y)×dxdy
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dyd(3y)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
3×dyd(y)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
3×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
3
3dxdy
3dxdy=dxd(−31x−35)
Calculate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−31x−35)
Use differentiation rules
dxd(−31x)+dxd(−35)
Evaluate the derivative
More Steps


Evaluate
dxd(−31x)
Use differentiation rule dxd(cf(x))=c×dxd(f(x))
−31×dxd(x)
Use dxdxn=nxn−1 to find derivative
−31×1
Any expression multiplied by 1 remains the same
−31
−31+dxd(−35)
Use dxd(c)=0 to find derivative
−31+0
Evaluate
−31
3dxdy=−31
Multiply by the reciprocal
3dxdy×31=−31×31
Multiply
dxdy=−31×31
Multiply
More Steps


Evaluate
−31×31
To multiply the fractions,multiply the numerators and denominators separately
−3×31
Multiply the numbers
−91
dxdy=−91
Take the derivative of both sides
dxd(dxdy)=dxd(−91)
Calculate the derivative
dx2d2y=dxd(−91)
Solution
dx2d2y=0
Show Solution

Graph